Yoga for Building Muscle Strength: The 5 Most Effective Poses for Every Level
In recent years, yoga has evolved from being solely associated with flexibility and relaxation to a robust fitness practice that promotes muscle strength and overall well-being. This article breaks down the most effective yoga poses that help strengthen muscles across different parts of the body, all while providing practical tips and insights on how to integrate them into your daily routine.
Introduction
When people think of strength training, yoga is not always the first thing that comes to mind. However, yoga can be an incredibly effective way to build muscle strength through bodyweight resistance, balance, and controlled movements. The key is to focus on poses that engage your core, arms, legs, and back—building endurance, stability, and power.
This guide will introduce five specific poses that not only strengthen different muscle groups but are also accessible to all levels, from beginners to advanced practitioners. You’ll learn how to integrate them into your routine, why they work, and how they fit within the larger context of your overall fitness goals.
Key Concepts
- Isometric holds: Maintaining static positions to engage muscles fully.
- Muscle endurance: Sustaining muscle contractions over time.
- Progressive overload: Gradually increasing the challenge of the pose.
- Core stability: Strengthening the muscles that support your spine.
- Mind-muscle connection: Developing awareness of muscle engagement during poses.
Historical Context
Yoga, with its roots in ancient India, has always been linked to spiritual growth and physical discipline. Traditionally, yoga practices focused on balance, flexibility, and controlled breathing, but modern adaptations have transformed yoga into a powerful tool for strengthening muscles. In the West, practitioners began modifying yoga for athletic conditioning in the mid-20th century, recognizing its potential for building endurance and muscle tone.
Current State Analysis
Today, yoga is a major component of many strength training routines. Athletes, trainers, and fitness enthusiasts use yoga to complement weightlifting and cardiovascular training. While resistance training with weights typically isolates muscle groups, yoga emphasizes full-body engagement—making it a holistic approach to strength development.
The following poses target specific muscles, but they also work synergistically to create balance and stability throughout the body.
Practical Applications: The 5 Best Yoga Poses for Muscle Strength
1. Plank Pose (Phalakasana)
Target Muscles: Core, shoulders, arms
The Plank Pose is a fundamental yoga posture that strengthens the core, shoulders, and arms. It teaches you to hold your body in a stable, aligned position using your own body weight.
- Beginner tip: Start with a modified plank by dropping your knees to the floor.
- Advanced variation: Increase intensity by holding the pose longer or lifting one leg.
2. Warrior II (Virabhadrasana II)
Target Muscles: Legs, glutes, hips, core
Warrior II is excellent for strengthening the lower body. This pose engages the quadriceps, glutes, and core muscles as you hold a deep lunge with your arms extended.
- Beginner tip: Keep your front knee aligned over the ankle to avoid strain.
- Advanced variation: Sink deeper into the lunge and hold for longer.
3. Chair Pose (Utkatasana)
Target Muscles: Quadriceps, glutes, back
Chair Pose mimics the motion of sitting back into a chair, requiring intense engagement of the legs and back. This posture is great for improving leg strength and core stability.
- Beginner tip: Don’t go too low at first; focus on maintaining your balance.
- Advanced variation: Reach your arms overhead for more core engagement.
4. Boat Pose (Navasana)
Target Muscles: Core, hip flexors
This pose works the abdominal muscles and hip flexors, enhancing your core strength. It is particularly beneficial for improving balance and posture.
- Beginner tip: Keep your knees bent if straightening the legs is too challenging.
- Advanced variation: Hold the pose longer or extend your legs for increased difficulty.
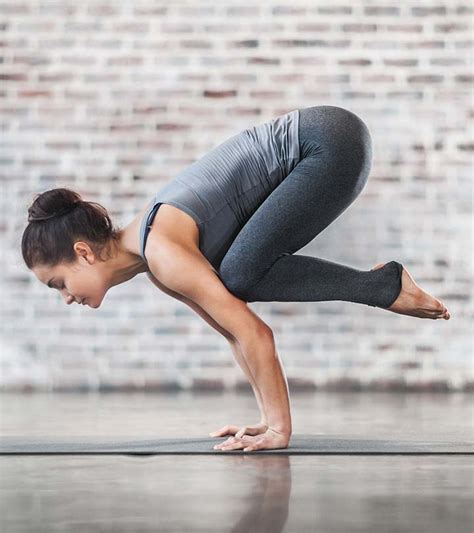
5. Crow Pose (Bakasana)
Target Muscles: Arms, shoulders, core
One of the most advanced poses, Crow Pose requires balance and core strength, while also building arm and shoulder strength. It’s a great way to challenge yourself as you progress in your practice.
- Beginner tip: Practice leaning forward into the pose without lifting your feet off the ground at first.
- Advanced variation: Transition from Crow Pose to a handstand.
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Yoga for Strength Building
| Case Study | Goal | Yoga Practice Focus | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Athlete recovering from injury | Rebuild muscle strength in lower body | Incorporating Warrior II and Chair Pose | Improved leg strength and core stability |
| Beginner seeking full-body strength | Increase core and upper body strength | Plank and Crow Pose focus | Noticeable improvement in core stability |
| Advanced practitioner | Challenge with balance and strength | Combining Crow Pose with handstand work | Better arm strength and overall balance |
Stakeholder Analysis
- Beginners: Will benefit from the accessibility of foundational poses.
- Advanced practitioners: Can challenge their strength and balance with more complex variations.
- Trainers and athletes: Yoga complements other strength-building exercises, offering full-body integration and injury prevention.
- Physical therapists: Often recommend yoga for strength recovery and rehabilitation.
Implementation Guidelines
- Begin with warm-up exercises to prepare the muscles for deeper engagement.
- Incorporate the five key poses into your routine, focusing on holding each for 30 seconds to 1 minute.
- Progress gradually by increasing the duration and intensity of each pose.
- Focus on form and alignment to prevent injury and maximize muscle engagement.
- Use props like yoga blocks to modify poses as needed, especially for beginners.
- Practice consistently for long-term muscle strengthening benefits.
Ethical Considerations
While yoga is generally safe for most individuals, it’s important to recognize the limitations and risks associated with pushing the body too far too fast. Proper guidance from certified instructors is key to avoiding injuries, especially when attempting advanced poses.
Limitations and Future Research
While yoga is an effective form of strength training, it may not entirely replace traditional weight training, particularly for those seeking to maximize muscle hypertrophy. More research is needed to compare the long-term benefits of yoga versus other strength-building modalities, especially across different populations (e.g., older adults, athletes).
Future research could explore the potential of yoga to improve muscle strength in clinical populations, such as those recovering from injury or illness. Additionally, more data is needed on how yoga affects muscle strength across different age groups and fitness levels.
Expert Commentary
Experts across fitness and health fields agree that yoga offers numerous benefits for muscle strengthening, particularly through its focus on core stability, balance, and full-body engagement. By combining dynamic and static holds, yoga promotes functional strength that supports everyday activities. For those looking to integrate more mindful practices into their fitness routines, yoga offers a holistic approach to building strength, flexibility, and mental focus simultaneously.