Choosing the Right Practice Intensity for Optimal Results: A Comprehensive Guide
Practice intensity plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of training, whether in sports, academics, or skill acquisition. Determining the correct intensity level involves balancing effort with recovery to maximize gains without causing burnout or injury. This guide explores the key concepts, historical context, current research, practical applications, and future implications of practice intensity.
Introduction
When it comes to improving performance, the intensity of practice is often a deciding factor. Too little effort, and progress stalls; too much, and the risk of burnout or injury rises. Finding the optimal practice intensity is essential for long-term success. This article outlines how to choose the right practice intensity, backed by historical trends, current research, and practical strategies.
Key Concepts
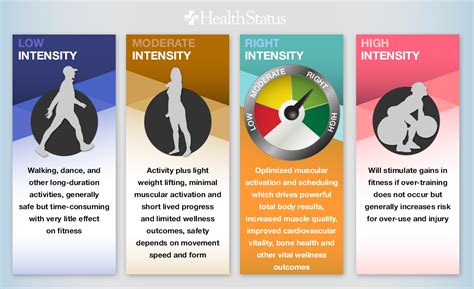
- Practice intensity: The level of physical or mental effort exerted during practice sessions.
- Optimal zone of practice: The sweet spot where practice is challenging but not overwhelming.
- Deliberate practice: Purposeful and structured practice designed to improve performance in a specific area.
- Overtraining: A state of fatigue and decreased performance caused by excessive practice without adequate recovery.
- Recovery: The period of rest or low-intensity activity that allows the body or mind to rejuvenate and improve from previous practice efforts.
Historical Context
The concept of practice intensity has evolved over time. In the early 20th century, physical training emphasized quantity over quality. Athletes and scholars alike were encouraged to practice long hours without much regard for intensity levels. As performance science progressed, the importance of structured practice and intensity management became clear. Soviet sports science in the mid-20th century was one of the pioneers in focusing on deliberate practice intensity, emphasizing the balance between effort and recovery.
Current State Analysis
Today, the debate continues around how much intensity is optimal. Current research suggests that practice intensity needs to be individualized. For example, a musician’s practice intensity may involve long periods of focused attention, while an athlete may require more frequent recovery sessions due to physical strain. The key is understanding that different domains require different intensity strategies.
Practical Applications
- Sports: High-intensity practice should be paired with periods of active recovery to prevent overtraining. Interval training is one approach to maintaining intensity without exhaustion.
- Academics: Intense study sessions followed by breaks (e.g., Pomodoro technique) can enhance focus and retention.
- Creative skills: Creative professionals often benefit from periods of intense work followed by relaxation to allow subconscious processing.
Case Studies
| Field | Practice Intensity | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Athletics | High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) | Improved cardiovascular and muscular endurance with reduced injury risk. |
| Music | Deliberate, focused practice for 90 minutes with breaks | Increased skill acquisition and performance under pressure. |
| Academics | Pomodoro Technique (25 min study, 5 min break) | Improved information retention and reduced cognitive fatigue. |
| Programming | Intensive coding sprints followed by peer reviews | Enhanced code quality and problem-solving skills. |
Stakeholder Analysis
The choice of practice intensity affects multiple stakeholders:
- Athletes: Must balance physical gains with injury prevention.
- Coaches: Responsible for tailoring training programs to individual needs.
- Students: Need to manage study habits to prevent burnout.
- Educators: Must design curricula that challenge without overwhelming.
Implementation Guidelines
For optimal practice intensity, follow these guidelines:
- Monitor progress: Use performance data to track improvements and adjust intensity as needed.
- Incorporate recovery: Plan for recovery sessions to maintain long-term gains.
- Individualize intensity: Tailor practice intensity to the person’s physical and mental capabilities.
- Use feedback loops: Implement regular feedback sessions to fine-tune intensity levels.
- Balance stress and rest: Ensure a balance between challenging practice and adequate rest to avoid burnout.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical concerns around practice intensity often center on balancing performance improvement with mental and physical well-being. Pushing individuals too hard can lead to negative outcomes, such as stress injuries or mental health challenges. Coaches, educators, and mentors must be mindful of the psychological and physiological limits of those they train, ensuring practice remains sustainable.
Limitations and Future Research
Current research on practice intensity is limited by the need for more longitudinal studies, especially in non-athletic fields like academics and the arts. Future research should investigate how different intensities affect long-term skill retention across diverse populations. Additionally, understanding the neurological basis for recovery and overtraining could provide deeper insights into how to optimize practice.
Expert Commentary
Experts agree that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to practice intensity. What works for one individual may not work for another, and even within the same discipline, the optimal intensity can vary based on goals, experience level, and personal limits. This guide provides a framework for understanding and applying practice intensity, but the best outcomes will always come from adapting these principles to individual needs. As research progresses, we can expect more sophisticated methods to emerge, further refining how we approach practice intensity for maximum performance.